internal energy, specifc heat capacity and specifc latent heat
Difficulty Levels:
1
Q&A
Medium
A heater supplies energy at a constant rate to $$0.045 \mathrm{~kg}$$ of a substance.The variation with time of the temperature of the substance is shown in Fig.3.1.The substance is perfectly insulated from its surroundings.
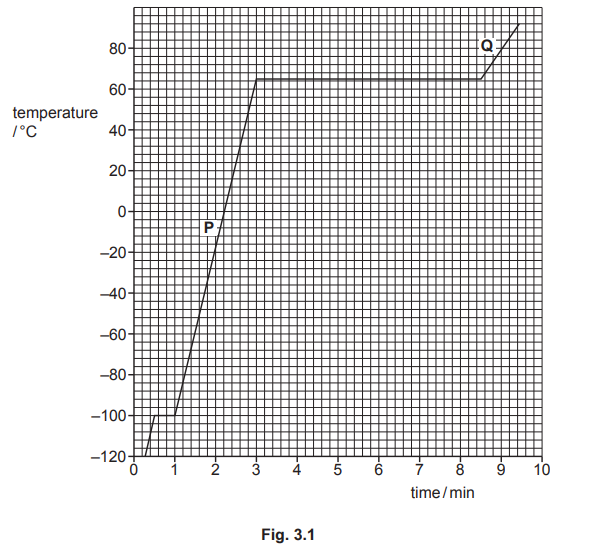 (i)Determine the temperature at which the substance melts.
temperature $$=$$ $$\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots { }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$
(ii)The power of the heater is $$150 \mathrm{~W}$$.
Use data from Fig.$$3.1$$ to calculate,in $$\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$$,the specific latent heat of vaporisation $$L$$ of the substance.
$$L=$$ $$\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots $$ $$\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$$ [3]
(iii)Suggest what can be deduced from the fact that section $$\mathbf{Q}$$ on the graph is less steep than section $$\mathrm{P}$$
(i)Determine the temperature at which the substance melts.
temperature $$=$$ $$\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots { }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$
(ii)The power of the heater is $$150 \mathrm{~W}$$.
Use data from Fig.$$3.1$$ to calculate,in $$\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$$,the specific latent heat of vaporisation $$L$$ of the substance.
$$L=$$ $$\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots $$ $$\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$$ [3]
(iii)Suggest what can be deduced from the fact that section $$\mathbf{Q}$$ on the graph is less steep than section $$\mathrm{P}$$
 (i)Determine the temperature at which the substance melts.
temperature $$=$$ $$\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots { }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$
(ii)The power of the heater is $$150 \mathrm{~W}$$.
Use data from Fig.$$3.1$$ to calculate,in $$\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$$,the specific latent heat of vaporisation $$L$$ of the substance.
$$L=$$ $$\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots $$ $$\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$$ [3]
(iii)Suggest what can be deduced from the fact that section $$\mathbf{Q}$$ on the graph is less steep than section $$\mathrm{P}$$
(i)Determine the temperature at which the substance melts.
temperature $$=$$ $$\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots { }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$
(ii)The power of the heater is $$150 \mathrm{~W}$$.
Use data from Fig.$$3.1$$ to calculate,in $$\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$$,the specific latent heat of vaporisation $$L$$ of the substance.
$$L=$$ $$\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots $$ $$\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}$$ [3]
(iii)Suggest what can be deduced from the fact that section $$\mathbf{Q}$$ on the graph is less steep than section $$\mathrm{P}$$ 
Answer:
(i)$$-100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$
(ii)$$\begin{aligned} \text { time } &=8.5-3.0 \\ &=5.5 \mathrm{~min} \end{aligned}$$
$$P t=m L$$
energy $$=$$ power $$x$$ time $$=150 \times 5.5 \times 60$$
$$
=49500 \mathrm{~J}
$$
$$L=\frac{E}{m}$$
$$=\frac{49500}{0.045}$$
$$=1100 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1}$$
(iii)gas has a higher specific heat capacity(than liquid)
Explanation:
2
Q&A
Medium
The specific latent heat of vaporisation is much greater than the specific latent heat of fusion for the same substance.
Explain this,in terms of the spacing of molecules.
Answer:
(much)greater increase in spacing of molecules(for vaporisation compared with fusion)
Explanation:
3
Q&A
Basic
Define specific heat capacity.[2]
Answer:
略
Explanation: